Health Committee of AACCDISanitary Platform————————————————————
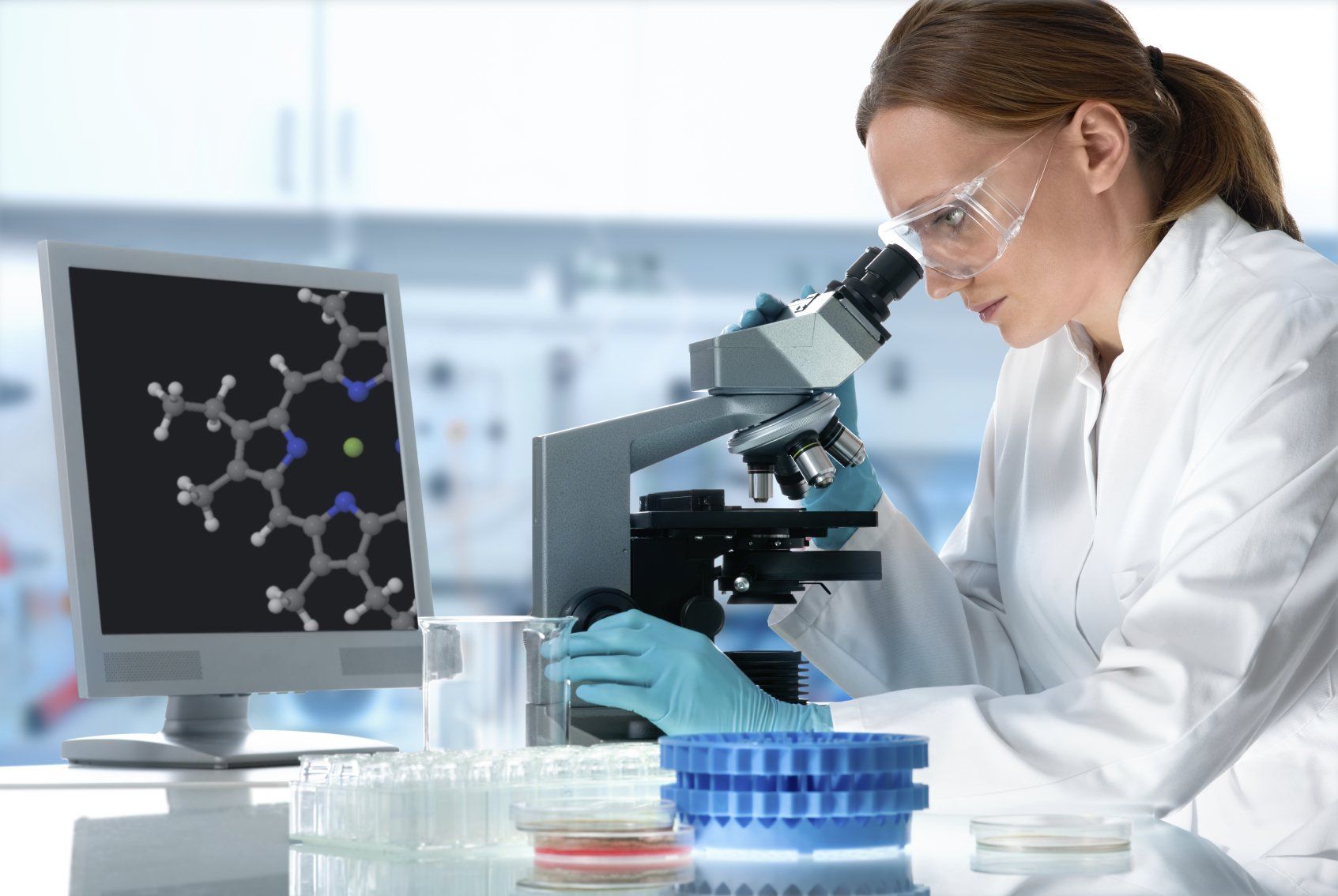

The clinical laboratory is the place where a multidisciplinary team made up of biochemists, molecular chemists, clinical analysts, pathologists, nefectologists, laboratory technicians and analysis technicians, develop and analyze human biological samples that contribute to the study, prevention, and research ( I * D) feasible for the development of drugs, diagnostic elements and equipment and management programs, related to the health especially of people and therefore animals. The clinical pathology laboratory uses the methodologies of various disciplines such as biochemistry - also called clinical chemistry - hematology, immunology, and microbiology. In the laboratory, various biological samples are obtained and studied, such as blood, urine, feces, synovial fluid (joints), cerebrospinal fluid, pharyngeal and vaginal exudates, among other types of samples.
- Hematology: In this section the complete blood count and various tests are performed to evaluate the values of the different components of the blood.
- Clinical biochemistry: Here, analyzes are performed that are classified as follows:
- Routine blood chemistry, covering multiple parameters such as the determination of glucose, cholesterol, etc.
- General urine tests
- Determination of gases in blood (partial pressure of oxygen, of anhydro-carbonic acid, reserve of bicarbonate, PH, etc.)
- Microbiology: The various tasks performed here can be classified as follows.
- Coproparasitology: Its purpose is to investigate the presence of parasites in fecal matter.
- Bacteriology: It consists of directly or indirectly examining the presence or activity of microscopic organisms in blood, urine, fecal matter, gastric juice and organic exudates.
- Immunology: In this section antibody determinations and other determinations are made in order to evaluate the immune system
- Hormones: This section discusses the different hormones in order to assess the endocrine system.
- Tumor markers: This section analyzes some parameters that increase or appear as part of tumor processes and that serve to detect different types of cancer and their evaluation during treatment.
CLINICAL FURNITURE
ELECTROMEDICINE
PHYSIOTHERAPY AND MASSAGE
ESTHETIC
STERILIZATION
DIAGNOSIS
DISPOSABLE
SURGICAL INSTRUMENTS
CREAMS OILS GELS
CLOTHING AND SAFETY
MEDICAL SCALES
LAMPS AND LOUPES
MEDICAL SIMULATORS
SPECIALTIES :
- (R&D) DNA
- PCR reagents (DNA / RNA)
- Quick Diagnostic Kit
- Sequencing equipment

If you have a clinic as a business, be it dental, ophthalmological, aesthetic, medical, etc. this article interests you. Because your business needs to be governed by the rules of health marketing. To do this, and first of all we need to clarify concepts. What is health marketing?
Health marketing is defined as all those non-intrusive commercial strategies whose work consists of capturing, accompanying until the final transaction and maintaining the loyalty of target patients.
The mistake of many healthcare companies is that they do not need a marketing plan. What is this negative perception of reality due to? The reason is none other than to confuse marketing with advertising. An action that is not considered very moral if we are talking about health. However, healthcare marketing doesn't have to be deceptive or lucrative. Quite the opposite. It is about offering a preventive and satisfactory vision, according to the needs of patients.
Evolution is part of all kinds of processes. And in this sense, health marketing was not going to be less. In recent years, we have seen a number of key changes for the development of healthcare marketing. The appearance of new technologies, as well as the change in the mentality of consumers have been a fundamental part of this entire process.
Analyzing its evolution and development we have found that:
- Health marketing plans first focused on professionals in the sector, then on the Health Administration and later they have turned their full attention to the needs of patients.
- The importance of developing services around products has been another of the key changes in health marketing.
- Greater rigor in the messages, as well as in the different marketing actions. We are talking about health. Therefore, this turn was extremely necessary to gain the confidence of the patients.
- The opening of new communication channels thanks to the appearance of new technologies (mHealth). Mobile applications are being one of the most important keys for the advancement of healthcare marketing.
A medical device is any instrument, device, equipment, computer program, material or other article, used alone or in combination, including computer programs intended by the manufacturer for specific diagnostic and / or therapy purposes and that intervene in its proper functioning, Intended by the manufacturer to be used in humans for the purpose of:
- Diagnosis, prevention, control, treatment or alleviation of a disease,
- Diagnosis, control, treatment, alleviation or compensation of an injury or a deficiency,
- Investigation, replacement or modification of the anatomy or a physiological process
- Regulation of conception and that it does not exert the main action that it is desired to obtain inside or on the surface of the human body by pharmacological, immunological, non-metabolic means, but to whose function it can contribute to such means.
In vitro diagnostic products are any medical device that consists of:
- A reactive, reactive product
- Caliper
- Control material
- Instrument and materials case
- Instrument, apparatus, equipment or system
Used alone or in association with others, intended by the manufacturer to be used in vitro for the study of samples from the human body, including blood and tissue donations, solely or primarily for the purpose of providing information
- Relating to a physiological or pathological state
- Relating to a congenital anomaly
- To determine safety and compatibility with potential recipients
- To monitor therapeutic measures
To be able to market this type of product, it is necessary to request the corresponding license for the installation and make the EU Declaration of Conformity and / or CE Certification of the product issued by a Notified Body (ON) in accordance with Regulation (EU) 2017/745 on Medical Devices and in accordance with Regulation (EU) 2017/746 on Medical Devices for In Vitro Diagnosis. To this end, the essential requirements that medical devices and in vitro diagnostic products and their accessories must meet are established, which refer to all aspects that may influence the safety of the products, including those of electromagnetic compatibility and protection of the radiation for the case of electromedical sanitary products.
Within the new social environment in which healthcare organizations are immersed, they must adopt new strategies to manage their logistics activity more efficiently, thus optimizing stock levels, delivery routes and the size required by hospital warehouses. In this article the concept of logistics unit is defined, the components of the hospital supply chain are analyzed, the impact of new technologies and the standardization or coding of health products in logistics are discussed, ending with the study of 4 cases through which the advantages and disadvantages of the implementation and execution of certain strategies for the operational management of logistics activity are observed.
Health Services are in a period of profound strategic change in response to demands for greater productivity and efficiency. Within this context, health authorities must achieve the dual objective of providing health and welfare services to the community, while at the same time developing new management control techniques that allow them to be more efficient and productive; all this with the ultimate goal that hospitals improve health processes and services and increase their value for citizens.
To date, hospital logistics managers have used different operational approaches developed over the years, focusing mainly on inventory management 1, but on many occasions, these operating methods were reactions to administrative constraints and rather than true strategies of a service. In many cases, logistics management is excluded from the original or primary design of new health facilities, and hospital administration is focused on units, research laboratories, surgical rooms, etc. Only after the construction and start-up of the healthcare activity have they concluded, do they proceed to design the logistics activity. In this context, an optimized management of the supply chain turns out to be impossible, opting in most cases for short-term solutions or for adopting long-term cooperative relationships with organizations outside the health entity itself.
As a result of globalization in this sector, healthcare and healthcare products companies are redesigning their approach to the transportation, warehousing, distribution and delivery of their products.

The business sector is dedicated to the manufacture, preparation and marketing of medical chemicals for the treatment and prevention of diseases. Some companies in the sector manufacture pharmaceutical chemicals and reagents in bulk (primary production), and prepare them for medical use through methods known collectively as secondary production or laboratories specialized in consolidating formulas and diagnostic elements. The highly automated secondary production processes include the manufacture of dosed drugs, such as tablets, capsules or sachets for oral administration, injectables, ovules and suppositories. Because its activity directly affects human health, this industry is subject to a wide variety of laws and regulations regarding research, patents, testing and marketing of drugs and diagnostic kits.
Many pharmaceutical companies carry out research and development (R&D) tasks in order to introduce new and improved treatments and diagnostic elements that are more sensitive, effective and faster in their detection. In some countries, each stage of testing of new drugs and reactive products with domestic animals (farm or laboratory) or with humans in the last phase of experimentation before being put on the market for human use and, has to receive the authorization of the national regulatory bodies of the countries or defined economic areas. If final approval occurs, authorization is granted to use them under specific conditions. [Citation required] In other countries, you can obtain permission to distribute a drug, or diagnostic elements, presenting the authorization of the country of origin, making the proper inscriptions in regulatory bodies.
Most countries grant patents for recently developed or modified medicines, drugs or diagnostic items for periods of about 15 years from the date of authorization.
Companies assign a trademark to their innovations, which become their exclusive property. In addition, new drugs are given an official, publicly owned generic name. After the patent expires, any company that meets the regulatory body's standards can manufacture and sell products under the generic name. In reality, the pharmaceutical industry is the main driver of the extension of the patent system, and has put pressure on developing countries to make them follow this system.
Most of the pharmaceutical companies and reagent laboratories have the character of helping patients internationally and are therefore present in many countries through subsidiaries. The technologically advanced sector employs many university graduates: pharmacists, microbiologists, biologists, biochemists, chemists, engineers, pharmacologists, physicians, physicists and veterinarians, and graduates in nursing. These professionals work in research and development (R&D), production, quality control, marketing, medical representation, public relations or general administration.

Contact the Health Committee of AACCDI
Leave us your information and we will get in touch with you.


